x264 帧类型决策
在lookahead阶段,帧的初始类型都被标记为X264_TYPE_AUTO。
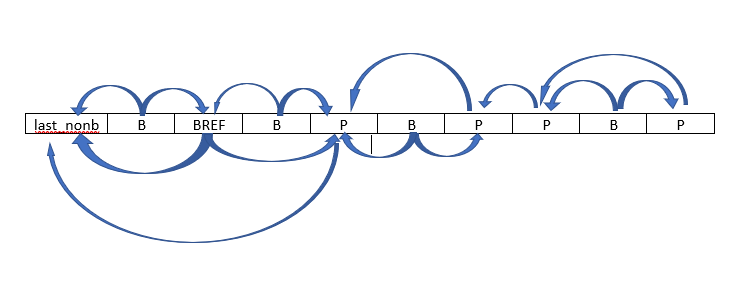
lookahead阶段的帧参考关系:
- P帧只参考紧邻的前一个I/P
- Bref帧参考紧邻的前一个I/P帧和紧邻的后一个I/P帧
- B帧参考紧邻的前一个I/P/Bref帧和紧邻的后一个I/P/Bref帧
IDR帧决策
B/P帧决策
在x264中有3种决策策略:
- X264_B_ADAPT_NONE
- X264_B_ADAPT_FAST
- X264_B_ADAPT_TRELLIS
这三种策略都会决策出B帧和P帧,但此时的B帧中还没有Bref。
X264_B_ADAPT_NONE
对给定的lookahead缓存帧,输出连续bframes数目的B帧加一个P帧,如此反复循环。
如果h->param.i_bframe为0,则全部决策为P帧。
// num_bframes为最大连续B帧个数
int num_bframes = h->param.i_bframe;
// num_frames为lookahead缓存帧个数
// frames[0]是上一次已经被决策出来的非B帧
for( int j = 1; j < num_frames; j++ )
{
// 要么h->param.i_bframe ==0, 则决策为全P帧
// 要么已经决策出来了的连续B帧个数达到最大h->param.i_bframe,则下一个决策为P帧
if( !num_bframes )
{
if( IS_X264_TYPE_AUTO_OR_B( frames[j]->i_type ) )
frames[j]->i_type = X264_TYPE_P;
}
else if( frames[j]->i_type == X264_TYPE_AUTO )
{
// 如果外部指定了j+1的帧类型为B,则j决策为P
if( IS_X264_TYPE_B( frames[j+1]->i_type ) )
frames[j]->i_type = X264_TYPE_P;
else
frames[j]->i_type = X264_TYPE_B;
}
// 决策了一个B帧,num_bframes就建议
if( IS_X264_TYPE_B( frames[j]->i_type ) )
num_bframes--;
else // 如果决策出了P帧,则重置num_bframes
num_bframes = h->param.i_bframe;
}
X264_B_ADAPT_FAST
B_ADAPT_FAST的策略是:对给定的lookahead缓存帧frames(其中frames[0]已经在上一轮决策中被决策为非B帧):
-
首先计算决策为BP和PP时的cost,取cost最小时的帧类型,当前帧决策结束。
注:加粗的帧类型为待决策的帧,且对于待决策的lookahead缓存帧队列,最后一帧的帧类型必定为P帧。
-
如果上一帧决策为B帧,则继续计算决策为[B]BP和[B]PP时的cost,取cost最小时的帧类型,当前帧决策结束。
注:中括号中的B帧个数为已经决策出来的B帧个数。
-
重复第2步决策,直到
- 上一帧决策为P帧;
- 已决策的B帧个数达到最大,则当前帧只能决策为P帧;
-
此时已经决策出P帧,则重置流程转到第一步,以P帧的下一帧为起始帧开始决策,直到lookahead中的所有缓存帧决策完毕。
int last_nonb = 0;
int num_bframes = h->param.i_bframe;
char path[X264_LOOKAHEAD_MAX+1];
for( int j = 1; j < num_frames; j++ )
{
// 决策了一个B帧,num_bframes就减一
if( j-1 > 0 && IS_X264_TYPE_B( frames[j-1]->i_type ) )
num_bframes--;
else // j-1被决策为P帧,重置last_nonb和num_bframes
{
last_nonb = j-1;
num_bframes = h->param.i_bframe;
}
// 已经决策出来了h->param.i_bframe个B帧了,则j只能决策为P
if( !num_bframes )
{
if( IS_X264_TYPE_AUTO_OR_B( frames[j]->i_type ) )
frames[j]->i_type = X264_TYPE_P;
continue;
}
// 由外部指定当前帧类型,跳过当前帧
if( frames[j]->i_type != X264_TYPE_AUTO )
continue;
// 如果外部指定了j+1的帧类型为B,则j决策为P
if( IS_X264_TYPE_B( frames[j+1]->i_type ) )
{
frames[j]->i_type = X264_TYPE_P;
continue;
}
//当前最多可以插入B帧的个数
int bframes = j - last_nonb - 1;
// 插入B帧
memset( path, 'B', bframes );
strcpy( path+bframes, "PP" );
// 计算B...B PP的cost
uint64_t cost_p = slicetype_path_cost( h, &a, frames+last_nonb, path, COST_MAX64 );
// 计算B...B BP的cost
strcpy( path+bframes, "BP" );
uint64_t cost_b = slicetype_path_cost( h, &a, frames+last_nonb, path, cost_p );
if( cost_b < cost_p )
frames[j]->i_type = X264_TYPE_B;
else
frames[j]->i_type = X264_TYPE_P;
}
关于cost的计算
x264使用
static uint64_t slicetype_path_cost( x264_t *h, x264_mb_analysis_t *a, x264_frame_t **frames, char *path, uint64_t threshold )
计算给定帧类型序列的字符串,函数原型
/// @brief 计算给定帧类型字符串path的cost
/// @param h 编码器handle
/// @param a analysis上下文
/// @param frames lookahead缓存帧队列,frames[0]为已经决策出来的非B帧
/// @param path 帧类型字符串,格式为:非B帧 + 若干个B帧 + 待决策帧类型[B或P] + P帧
/// @param threshold 如果在计算过程中,当前的cost已经大于阈值threshold,则提前终止
/// @return 计算出来的cost
static uint64_t slicetype_path_cost( x264_t *h, x264_mb_analysis_t *a, x264_frame_t **frames, char *path, uint64_t threshold )
具体计算cost的过程:
-
记frames[0]为cur_nonb
- 从cur_nonb开始,找到下一个非B帧,记为next_nonb(P帧或I帧)
- 如果next_nonb为P帧,计算next_nonb参考cur_nonb的inter_cost;如果next_nonb为I帧,计算next_nonb的intra_cost。
- 计算cur_nonb和next_nonb之间的每个B帧的inter_cost
- 如果禁用Bref,则计算每个B帧参考cur_nonb和next_nonb的inter_cost
- 如果使能Bref,则取B帧中最中间的B帧作为Bref,记为Bmid,然后计算:
- Bmid参考cur_nonb和next_nonb的inter_cost
- [B…Bmid)参考cur_nonb和Bmid的inter_cost
- (Bmid…B]参考Bmid和next_nonb的inter_cost
- 将next_nonb + 1作为cur_nonb,重复1,2,3步骤,直到path中的所有帧计算完成。
- 累加所有计算出来的cost作为当前path帧结构的cost。
X264_B_ADAPT_TRELLIS
B_ADAPT_TRELLIS基于Vertibi算法的算法实现,Vertibi算法是一种动态规划算法,其核心思想就是:问题的最优解如果可以由子问题的最优解推导得到,则可以先求解子问题的最优解,再构造原问题的最优解;若子问题有较多的重复出现,则可以自底向上从最终子问题向原问题逐步求解。
如果我们要决策出长度为length的缓存帧队列的最优帧结构,首先就要决策出长度为n(n < length)的缓存帧队列的最优帧结构。
-
假设此时我们已经得到了长度为0、1 、2、……、length- 2、 length - 1时的缓存帧队列的最优帧结构。
-
然后分别在长度为0的最优帧结构和最后一个P中间填充length-1个B帧计算cost,在长度为1的最优帧结构和最后一个P中间填充length-2个B帧计算cost,
……在长度为length-2的最优帧结构和最后一个P中间填充1个B帧计算cost,在长度为length-1的最优帧结构和最后一个P中间填充0个B帧计算cost
-
再所有计算出来的cost中取最小值,对应的帧结构即为长度为length时的缓存帧队列的最优帧结构。
上面就是B_ADAPT_TRELLIS的的核心思想。
我们记数组best_paths作为给定帧长度的队列的最优帧结构,最优即表示当前帧结构的cost最小。
显然我们可以得到:
- best_paths[0] = “”
- best_paths[1] = “P”
基于以上前提,对给定长度length的缓存帧队列(其中frames[0]已经在上一轮决策中被决策为非B帧,frames[length - 1]必定被决策为P帧),B_ADAPT_TRELLIS决策的流程可总结为以下步骤:
- 从n == 2开始循环计算,直到n == length。
- 获取帧个数为n-1时的最优帧结构best_paths[n-1],在best_paths[n-1]和P之间插入0个B帧,计算best_paths[n-1] + “P” 时的cost
- 获取帧个数为n-2时的最优帧结构best_paths[n-2],在best_paths[n-2]和P之间插入1个B帧,计算best_paths[n-2] + “BP”的cost
- 重复1,2步计算(重复的次数受到h->param.i_bframe的限制,最多计算MIN( h->param.i_bframe+1, length )次)
- 获取帧个数为1时的最优帧结构best_paths[1],在best_paths[1]和P之间插入n-2个B帧,计算best_paths[1] + “B repeat n-2” + “P”的cost
- 获取帧个数为0时的最优帧结构best_paths[0],在best_paths[0]和P之间插入n-1个B帧,计算best_paths[1] + “B repeat n-1” + “P”的cost
- 得到cost最小时的帧结构,保存在best_paths[n]中
经过上述计算,我们就得到了对给定长度length的缓存帧队列的最优帧结构best_path[length]。
for( int j = 2; j <= num_frames; j++ ) {
slicetype_path( h, &a, frames, j, best_paths );
}
static void slicetype_path( x264_t *h, x264_mb_analysis_t *a, x264_frame_t **frames, int length, char (*best_paths)[X264_LOOKAHEAD_MAX+1] )
{
char paths[2][X264_LOOKAHEAD_MAX+1];
int num_paths = X264_MIN( h->param.i_bframe+1, length );
uint64_t best_cost = COST_MAX64;
int best_possible = 0;
int idx = 0;
/* Iterate over all currently possible paths */
for( int path = 0; path < num_paths; path++ )
{
/* Add suffixes to the current path */
int len = length - (path + 1);
memcpy( paths[idx], best_paths[len % (X264_BFRAME_MAX+1)], len );
memset( paths[idx]+len, 'B', path );
strcpy( paths[idx]+len+path, "P" );
int possible = 1;
for( int i = 1; i <= length; i++ )
{
int i_type = frames[i]->i_type;
if( i_type == X264_TYPE_AUTO )
continue;
if( IS_X264_TYPE_B( i_type ) )
possible = possible && (i < len || i == length || paths[idx][i-1] == 'B');
else
{
possible = possible && (i < len || paths[idx][i-1] != 'B');
paths[idx][i-1] = IS_X264_TYPE_I( i_type ) ? 'I' : 'P';
}
}
if( possible || !best_possible )
{
if( possible && !best_possible )
best_cost = COST_MAX64;
/* Calculate the actual cost of the current path */
log_trace("[lookahead][slicetype-path]calculate cost of path[%d]:%s", idx, paths[idx]);
uint64_t cost = slicetype_path_cost( h, a, frames, paths[idx], best_cost );
if( cost < best_cost )
{
best_cost = cost;
best_possible = possible;
idx ^= 1;
}
}
}
/* Store the best path. */
memcpy( best_paths[length % (X264_BFRAME_MAX+1)], paths[idx^1], length );
}